Identity
For everyone and everything.

Background
Identity. It's a universal right.
Recognition of skills gained (skills identity) leads to economic identity.
Economic identity of individuals leads to a better society (collective).
The selfdriven identity framework helps with ...
- Creating identities for people, organisations and things.
- Assigning skill attributes as per the selfdriven Universal Skills Set.
- Sharing and verifing skills; helping with trust between learning partners (people and organisations) that don't know each other i.e. don't have existing established trust.
- Creating "On-Chain" identity; powered by Cardano.
- Linking to existing "On-Chain" Decentralised ID (DID) frameworks.
What
We are delivering on the following three key outcomes.
Identity
What is identity?
selfdriven IDs
The selfdriven SDI identity tokens.
Verification
The process by which a person or organisation ("learning-partner") that can verify the learner experience and assign the skills gained etc.
Issuing
Issuing of identity and verified achievements & skills.
Working With Others
The selfdriven Identity Protocol/Framework works well with others.
Sovereign State Issued Credentials
Working with state/sovereign issued frameworks national credentials etc
Identity
Who or What is It?
- Unchangeable Attributes; Date of Birth etc.
- Changeable Attributes; Skills etc
- Can be any type of entity; Individuals, Organisations (including DAOs) and Things (Real-World and Digital).
Digital Identity
- Tokenisation (Representation) of Identity.
- Attributes are via claims; Digital Verifiable Credentials (VCs)
- Digital Verifiable Credentials (VCs) are used to share attributes and build trust between entities.
Self-Sovereign Identity
(SSI)
Decentralised Identifiers
(DIDs)
- Are controlled by the entities that hold them.
- Enable cryptographic authentication of the DID holder.
- Describe the discovery of information needed to launch secure and privacy-preserving communication methods.
- Give access to service-independent data portability.
W3C DIDs Core Specification
Using Existing Trust Frameworks
selfdriven IDs
SDI
SDI Types
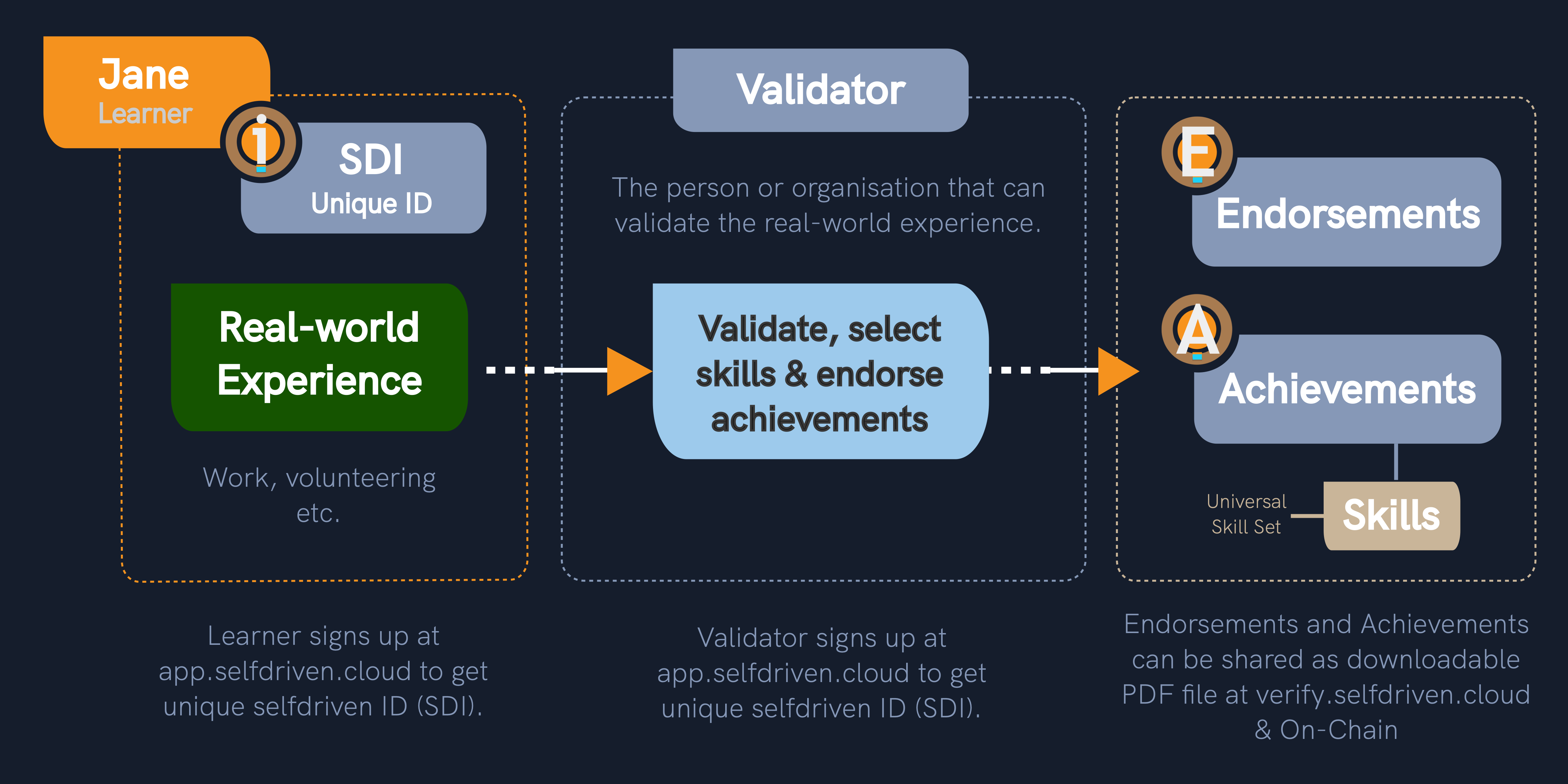
Verification
Example Process of Learning Partner Verifing Achievements & Endorsements
Issuing
Identity
Skills
Verifing the selfdriven Tokens (NFTs) as a Consumer
Example Verification of Skills Using the SDV Token
Checking the SDV Token Identifier Attribute
- sha256; [SDI]-[Attribute]-[Value]
- sha256-sdvk; [SDI]-[Attribute]-[Value]-[SDVk]
- aes256; [SDI]-[Attribute]-[Value]
SDV Identified Attributes Structure
"sha256", "sha512", "sha256-sdvk", "sha512-sdvk", "aes256", "pem"
"uri", "communication", "geolocation", "service", "cardano", "avatar", "website", "did"
"email", "usi", "mobile", "address", "transaction", "uxto", "url", "name", "w3c", "public-key-rsa-spki", "hash"
Working With Others
Identity Tokens, Protocols & Services
Services
Sovereign State Issued Credentials
National Identity
Credentials & Education Wallets, Passports etc
Self-Sovereign Identity
Methods
Trust
Establishing trust on-cloud (off-chain) & on-chain. For Everyone and everything.
Governance
How we improve, make decisions & establishing trust.
Tokens
selfdriven "On-Chain" tokens/assets.
Skills
Explore the universal skills set.
Help
Talk to us about any help you may need.
Decentralised Identifiers (DIDs)
"URL-based identifiers (URIs) in use on the Web today (2019) require that the identifier be leased from an authority such as a Domain Name Registrar. A Decentralized Identifier (DID) is an identifier that does not need to be leased; its creation and use is possible without a central authority to manage it. The advent of Blockchains and Decentralized Ledger Technologies have led to other innovations that support this new type of decentralized URI. DIDs have various benefits over more traditional URIs." - W3C - More...